Rebains' Portholefish, Diplophos rebainsi Krefft & Parin 1972
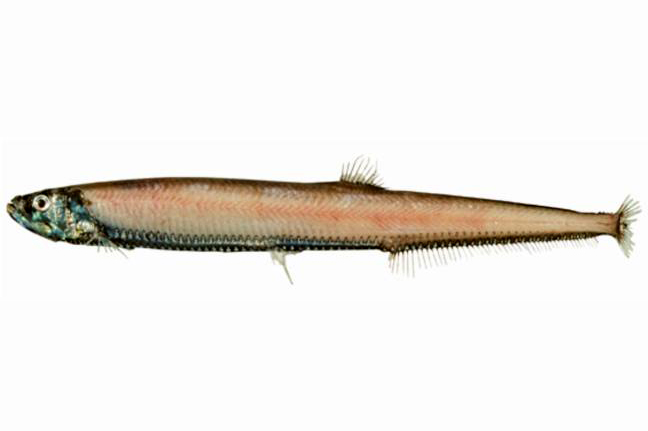

Rebains' Portholefish, Diplophos rebainsi. Source: Australian National Fish Collection, CSIRO. License: CC By Attribution-NonCommercial
Summary:
A porthole fish with the ventral photophore series beginning below the rear of the eye, 30-35 ventral photophores from the anal-fin origin to the caudal fin, fang-like teeth in the lower jaw, and comb-like teeth in the upper jaw.
Cite this page as:
Bray, D.J. 2020, Diplophos rebainsi in Fishes of Australia, accessed 25 Apr 2024, https://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/3928
Rebains' Portholefish, Diplophos rebainsi Krefft & Parin 1972
More Info
|
Distribution |
South of Point Hicks, Victoria, around Tasmania to south of Portland, Victoria. Elsewhere the species is circumglobal in southern seas (except Indian Ocean). Inhabits mesopelagic and bathypelagic waters at depths to 2000m. |
|
Features |
Dorsal fin 11-13; Anal fin 47-53; Pectoral fin 9; Pelvic fin 8-9; Branchiostegal rays 10-11; Total Gill rakers 12-13; Vertebrae 74-77. Vomer with 1-2 teeth on each side; 5-9 palatine teeth in single row; 2 small hooked teeth on anterior portion of tongue. Photophores: ORB 1 (below front margin of eye), OP 3, SO 1, BR7-8, IV 31-35, VAV 15-17, AC 32-34, IC 80-83, OA 60-63. Single photophore on lateral surface of dentary; 1 pre-P nonserial primary photophore. No minute photophores anterior to SO; interspace between last 2 AC about equal to preceding interspace. D origin nearer C base than snout. |
|
Biology |
reportedly spawns in the Austral Spring-Summer season. |
|
Similar Species |
|
|
Etymology |
The species is in honour of Eduard Rebains, the captain of the Soviet research vessel Akademic Kurchatov that collected the type specimen. |
|
Species Citation |
Diplophos rebainsi Krefft & Parin 1972, Archiv für Fischereiwissenschaft 23(2): 94, fig. 1. Type locality: Southwestern Atlantic, 43°00'S, 26°37'W, depth 900-1030 m. |
|
Author |
Bray, D.J. 2020 |
|
Resources |
Rebains' Portholefish, Diplophos rebainsi Krefft & Parin 1972
References
Flynn, A. & Pogonoski, J.J. 2012. Guide to Mesopelagic Fishes of the Southern Tasman Sea. Hobart, Australia : CSIRO Marine & Atmospheric Research, 221 pp. https://doi.org/10.4225/08/584af4b007924
Harold, A.S. & Gomon, M.F. 2008. Family Gonostomatidae in Gomon, M.F., Bray, D.J. & Kuiter, R.H. (eds) 2008. Fishes of Australia's Southern Coast. Sydney : Reed New Holland 928 pp.
Harold, A. & Milligan, R. 2019. Diplophos rebainsi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T135432746A135579477. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T135432746A135579477.en. Downloaded on 27 August 2020.
Johnson,R.K. 1970. A new species of Diplophos (Salmoniformes: Gonostomatidae) from the Western Pacific. Copeia 1970: 437-443.
Kenaley, C.P. & Stewart, A.L. 2015. Family Gonostomatidae. pp. 421–530 in Roberts, C.D., Stewart, A.L. & Struthers, C.D. (eds) The Fishes of New Zealand. Wellington : Te Papa Press Vol. 2 pp. 1-576.
Koeda, K. & Ho, H.-C. 2019. A new portholefish of the genus Diplophos (Stomiiformes: Gonostomatidae) from the western Pacific Ocean. pp. 107-113, in Ho, H.-C., Koeda, K. & Hilton, E.J. (eds) Study on the fish taxonomy and diversity of Taiwan. Zootaxa 4702(1) https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4702.1.15
Krefft, G. & Parin, N.V. 1972. Ergebnisse der Forschungsreisen des FFS "Walther Herwig" nach Südamerica. XXV. Diplophos rebainsi n. sp. (Osteichthyes, Stomiatoidei, Gonostomatidae), a new gonostomatid fish from southern seas. Archiv für Fischereiwissenschaft 23(2): 94-100 figs 1-2.
May, J.L. & Blaber, S.J.M. 1989. Benthic and pelagic fish biomass of the upper continental slope off eastern Tasmania. Marine Biology 101(1): 25.
Ozawa, T., Oda, K. & Ida, T. 1990. Systematics and distribution of the Diplophos taenia species complex (Gonostomatidae), with a description of a new species. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology 37: 98–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02905378
Robertson, D.A. 1975. Diplophos rebainsi Krefft & Parin, 1972, an addition to the mesopelagic fish fauna of New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 9(3): 411-415.
Schaefer, S., Johnson, R.K. & Badcock, J. 1986. Gonostomatidae. pp. 247–253 in Smith, M.M. & Heemstra, P.C. (eds) 1986. Smith's Sea Fishes. Johannesburg : Macmillan South Africa xx + 1047 pp. 144 pls. See ref at BHL
Spanovskaya, V.D. & Grigorash, V.A. 1979. Gonostomatids (Fam. Gonostomatidae) of the Australian-New Zealand region. Trudy Instituta Okeanologii. Akademiya Nauk SSSR. Moskva 106: 57-68 figs 1-2 [in Russian]
Williams, A. & Koslow, J.A. 1997. Species composition, biomass and vertical distribution of micronekton over the mid-slope region off southern Tasmania, Australia. Marine Biology 130: 259-276.
Young, J.W., Hobday, A.J., Campbell, R.A., Kloser, R.J., Bonham, P.I., Clementson, L.A. & Landsdell, M.J. 2011. The biological oceanography of the East Australian Current and surrounding waters in relation to tuna and billfish catches off eastern Australia. Deep-sea Research II 58: 720-733.