- Classification
- ACTINOPTERYGII
- ATHERINIFORMES
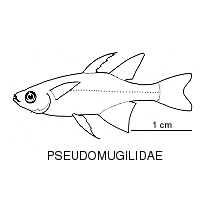
- PSEUDOMUGILIDAE
-
Fish Classification
-
Class
ACTINOPTERYGII Ray-finned fishes -
Order
ATHERINIFORMES Hardyheads -
Family
PSEUDOMUGILIDAE Blue eyes
Family PSEUDOMUGILIDAE
More Info
|
Family Taxonomy |
The family contains two genera and approximately 15 species; 7 species are known from Australia. The blue-eyes were reviewed by Allen & Cross (1982) and Saeed, Ivantsoff & Allen (1989), and were previously grouped with the family Melanotaeniidae or rainbowfishes. |
|
Family Distribution |
Blue-eyes are found in coastal drainages of northern and eastern Australia, and on Papua New Guinea, Irian Jaya and on several surrounding islands. Although most species inhabit freshwater streams, lakes, swamps, some are also found in tidal mangrove creeks, estuaries and even in marine areas on offshore islands. |
|
Family Size |
To 5 cm SL. |
|
Family Feeding |
Omnivores, feeding on microcrustaceans, small insects and algae. |
|
Family Reproduction |
Often breed year-round, with females attaching their adhesive eggs to vegetation. |
|
Family Commercial |
Blue-eyes are popular aquarium fishes and a number of species are available in the aquarium industry. |
|
Family Conservation |
A number of species are listed in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (IUCN Red List). |
|
Author |
Dianne J. Bray |
References
Allen, G.R. 1989. Freshwater fishes of Australia. T.F.H. Publications, Inc., Neptune City, New Jersey.
Allen, G.R. & Cross, N.J. 1982. Rainbowfishes of Australia and Papua-New Guinea. New Jersey : T.F.H. Publications 142 pp. figs.
Allen, G.R., S.H. Midgley & M. Allen. 2002. Field guide to the freshwater fishes of Australia. Western Australian Museum, Perth, Western Australia. 394 p.
Ivantsoff, W. 1999. Order Atheriniformes. Pseudomugilidae. Blue eyes. p. 2109-2112. In : K.E. Carpenter, K.E. & V.H. Niem (eds.) FAO species identification guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of the Western Central Pacific. Volume 4. Bony fishes part 2 (Mugilidae to Carangidae). FAO, Rome.
Merrick, J.R. & G.E. Schmida. 1984. Australian freshwater fishes: biology and management. Griffin Press Ltd., South Australia. 409 p.
Saeed, B., Ivantsoff, W. & Allen, G.R. 1989. Taxonomic revision of the family Pseudomugilidae (Order Atheriniformes). Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 40: 719–787.
White, B.N., R.J. Lavenberg & G.E. McGowen. 1984. Atheriniformes: development and relationships. p. 355-362. In Moser et al. Ontogeny and systematics of fishes. Spec. Publ. Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. (1): 1-760.
Wong, B.B.M., J.S. Keogh & D.J.M Glashan. 2004. Current and historical patterns of drainage connectivity in eastern Australia inferred from population genetic structuring in a widespread freshwater fish Pseudomugil signifer (Pseudomugilidae) Molecular Ecology 13: 391–401.