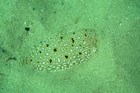
Southern Peacock Sole, Pardachirus hedleyi Ogilby 1916
Other Names: Peacock Sole, Rauther's Sole
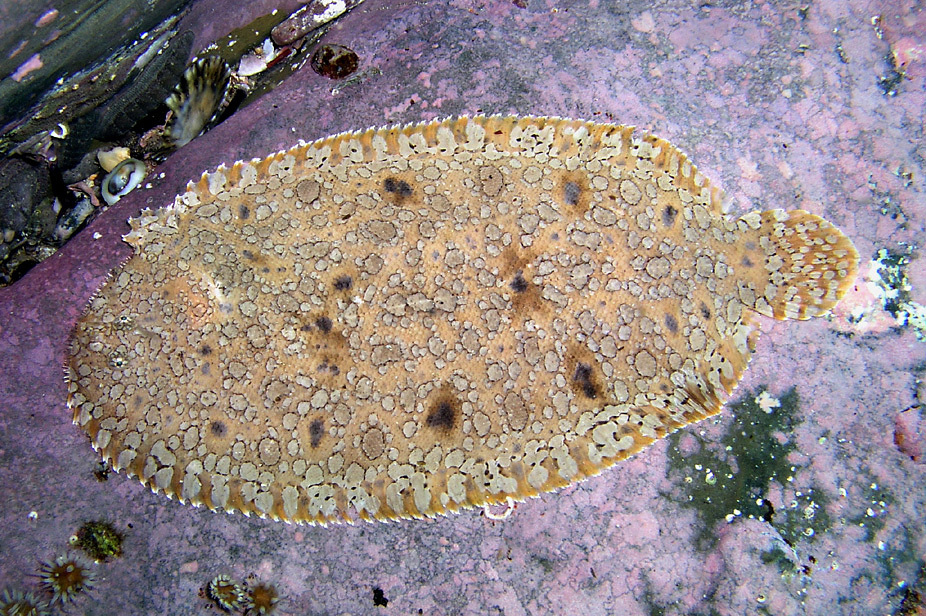

A Southern Peacock Sole, Pardachirus hedleyi, at Port Kembla, New South Wales, June 2005. Source: Sascha Schultz / iNaturalist.org. License: CC by Attribution-NonCommercial
Summary:
A brownish sole with dark-edged white blotches and scattered darker blotches on the upper side.
Cite this page as:
Bray, D.J. 2020, Pardachirus hedleyi in Fishes of Australia, accessed 01 Jul 2025, https://fishesofaustralia.net.au/Home/species/1008
Southern Peacock Sole, Pardachirus hedleyi Ogilby 1916
More Info
|
Distribution |
Endemic to eastern Australia, from Townsville, Queensland, to Tathra, New South Wales. Usually inhabits clear sandy areas in sheltered coastal waters. |
|
Features |
Body covered in small ctenoid scales; eyes positioned close together on right side of body, lower eye positioned immediately behind the mouth; nostrils on ocular side positioned at the end of a long tube; a fringe of filaments on the snout. |
|
Remarks |
Toxin glands are visible as pores along the bases of the dorsal and anal fins. |
|
Etymology |
Ogilby named the species hedleyi "... after my friend Charles Hedley, the premier conchologist of Australia". |
|
Species Citation |
Pardachirus hedleyi Ogilby 1916, Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 5: 144, pl. 17. Type locality: Port Jackson, New South Wales, and Moreton Bay, Queensland. |
|
Author |
Bray, D.J. 2020 |
|
Resources |
Southern Peacock Sole, Pardachirus hedleyi Ogilby 1916
References
Clark, E. & George, A. 1979. Toxic soles, Pardachirus marmoratus from the Red Sea and P. pavoninus from Japan, with notes on other species. Environmental Biology of Fishes 4( 2): 103-123.
Johnson, J.W. 1999. Annotated checklist of the fishes of Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 43(2): 709-762
Kuiter, R.H. 1993. Coastal Fishes of South-eastern Australia. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 437 pp.
Kuiter, R.H. 1996. Guide to Sea Fishes of Australia. A comprehensive reference for divers and fishermen. Sydney, NSW, Australia : New Holland Publishers xvii, 434 pp.
Kuiter, R.H. 2000. Coastal Fishes of South-eastern Australia. Gary Allen. 437 pp.
Munroe, T.A. 2001. Soleidae, Cynoglossidae. pp. 3878-3901 in Carpenter, K.E. & Niem, T.H. (eds). The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific. FAO Species Identification Guide for Fisheries Purposes. Rome : FAO Vol. 6 pp. 3381-4218.
Ogilby, J.D. 1916. Edible fishes of Queensland. Parts 4–9. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 5: 127-177 pls 14-23 Ref. at BHL
Randall, J.E. & Johnson, J.W. 2007. Revision of the soleid fish genus Pardachirus. Indo-Pacific Fishes 39: 1-22
Thomson, J.M. 1978. A Field Guide to the Common Sea & Estuary Fishes of Non-tropical Australia. Sydney : Collins 144 pp.