- Classification
- CHONDRICHTHYES
- ORECTOLOBIFORMES
- ORECTOLOBIDAE
-
Fish Classification
-
Class
CHONDRICHTHYES Sharks, rays ... -
Order
ORECTOLOBIFORMES -
Family
ORECTOLOBIDAE Wobbegongs
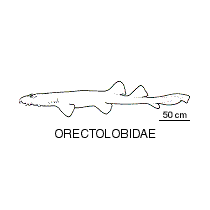
Family ORECTOLOBIDAE
A small group of well-camouflaged bottom-dwelling ambush predators.
More Info
|
Family Taxonomy |
The family comprises three genera and 11 species, and all genera and 10 species are known from Australian waters. |
|
Family Distribution |
Wobbegongs are found tropical to temperate seas of the Western Pacific, from Japan to Australia. They inhabit coral and rocky reefs in depths to 280 metres, although most species are found on the upper continental shelf. |
|
Family Description |
Species Wobbegons All species have barbels before the mouth and some have tentacular structures on other parts of the body. |
|
Family Size |
Range in length from 60 to 300 cm. |
|
Family Feeding |
Wobbegongs are sit-and-wait ambush predators, and usually feed at night on a range of fishes and invertebrates. |
|
Family Reproduction |
Some species give birth to live young and are ovoviviparous with the young hatching from eggs within the uterus. Other species are oviparous, and females lay oval-shaped eggs. |
|
Family Remarks |
Studies into visual capabilities of wobbegong sharks showed that the wobbegong visual system contains only a single class of cone photoreceptor. Cone receptors are the retinal cells used for vision under bright light conditions, whereas as rod photoreceptors are used in dim light. The researchers found that the eyesight of Western Wobbegongs and Ornate Wobbegongs was suited to both day and night vision, whereas O. maculatus and O. parvimaculatus had eyesight more suited to low light conditions. (Theiss et al. 2010) |
|
Author |
Dianne J. Bray |
References
Bass, A.J., D'Aubrey, J.D. & Kistnasamy, N. 1975. Sharks of the east coast of southern Africa. Part 4. The families Odontaspididae, Scapanorhynchidae, Isuridae, Cetorhinidae, Alopiidae, Orectolobidae and Rhiniodontidae. Investigational Report. Oceanographical Research Institute, Durban 39 1-102 figs 1-24 pls 1-15
Compagno, L.J.V. 1973. Interrelationships of living elasmobranchs. Journal of the Linnean Society of London, Zoology 53(suppl. 1): 15-61 pls 1-2
Compagno, L.J.V. 1984. FAO Species Catalogue. Sharks of the World. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Hexanchiformes to Lamniformes. FAO Fisheries Synopsis No. 125. Rome : FAO Vol. 4(1) pp. 1-249
Compagno, L.J.V. 2001. Sharks of the World. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Bullhead, mackerel and carpet sharks (Heterodontiformes, Lamniformes and Orectolobiformes). Rome : FAO, FAO Species Catalogue for Fisheries Purposes No. 1 Vol. 2 269 pp.
Compagno, L.J.V., Dando, M. & Fowler, S. 2005. A Field Guide to the Sharks of the World. London : Collins 368 pp.
Corrigan, S. & Beheregaray, L.B. 2009. A recent shark radiation: molecular phylogeny, biogeography and speciation of wobbegong sharks (family: Orectolobidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 52: 205-216
Goto, T. 2001. Comparative anatomy, phylogeny and cladistic classification of the order Orectolobiformes (Chondrichthyes, Elasmobranchi). Memoirs of the Graduate School of Fisheries Sciences, Hokkaido University 48(1): 1-100
Last, P.R. & Stevens, J.D. 1994. Sharks and Rays of Australia. Canberra : CSIRO Australia 513 pp. 84 pls [125]
Last, P.R. & Stevens, J.D. 2009. Sharks and Rays of Australia. Collingwood : CSIRO Publishing Australia 2, 550 pp. [132]
Ogilby, J.D. & McCulloch, A.R. 1908. A revision of the Australian Orectolobidae. Journal and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales 42: 264-299 fig. 1 pls 42-43
Regan, C.T. 1908. A revision of the sharks of the family Orectolobidae. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1908: 347-364 figs 11-13
Theiss, S.M., S.P. Collin & N.S. Hart. 2010. Interspecific Visual Adaptations among Wobbegong Sharks (Orectolobidae). Brain Behav Evol 76: 248-260.
Theiss, S.M., Collin, S.P., Hart, N.S. 2011, Morphology and distribution of the ampullary electroreceptors in wobbegong sharks: implications for feeding behaviour', Marine Biology 158: 723-735.
Theiss, S.M., W.I.L. Davies, S.P. Collin, D.M. Hunt & N.S. Hart. 2012. Cone monochromacy and visual pigment spectral tuning in wobbegong sharks. Biology Letters Online first: doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2012.0663