Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse, Hippocampus pontohi Lourie & Kuiter 2008
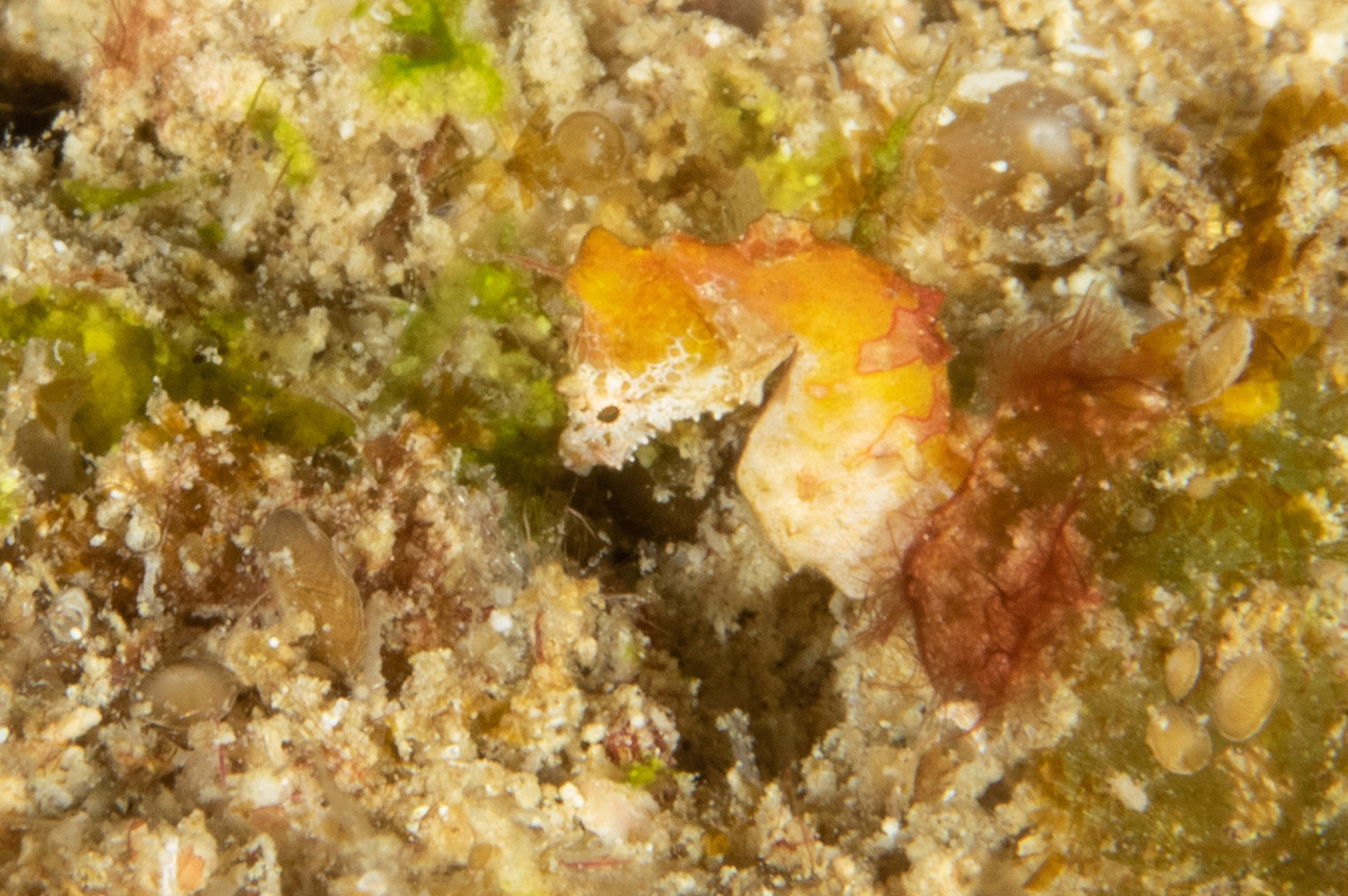

Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse, Hippocampus pontohi, in Fiji, December 2018. Source: Mark Rosenstein / iNaturalist.org. License: CC by Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
A brown pygmy seahorse scattered with white dots and sometimes with a marbled pattern, a bright red patch on the trunk, and a pale tail with brown bands.
Video of Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse at Bangka Island, Indonesia (as Severn's Seahorse, Hippocampus severnsi, which is a junior synonym of H. pontohi).
Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse, Hippocampus pontohi Lourie & Kuiter 2008
More Info
|
Distribution |
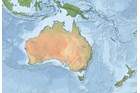
Recorded in Australia from Milin Reef, Great Barrier Reef, off Cairns, Queensland. Elsewhere the species occurs in the tropical East-Indo-west Pacific, from Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Solomon Islands, Fiji and the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Inhabits coral reefs, usually clinging in pairs to a variety of invertebrate hosts including coralline algae, bryozoans, hydrozoans and gorgonian corals (octocorals) - especially the coralline algae Halimeda and the hydroid Aglaephenia cupressina. The various host species were studied by Reijnen et al. (2011). |
|
Features |
|
|
Size |
An extremely small seahorse: height 13 mm, standard length 15 mm. |
|
Colour |
|
|
Feeding |
|
|
Biology |
Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse a relatively active pygmy seahorse and is commonly seen in pairs. Males brood the developing embryos, and two pregnant males each contained 11 embryos (Lourie & Kuiter 2008). |
|
Fisheries |
|
|
Conservation |
Data Deficient on the IUCN Red List of Threatened species. |
|
Remarks |
Hippocampus severnsi is a junior synonym of H. pontohi. However, H. pontohi, may be a junior synonym of Coleman's Seahorse, H. colemani (Lourie et al. 2016). |
|
Similar Species |
|
|
Etymology |
Named in honour of Hence Pontoh, the Indonesian dive guide who first brought these pygmy seahorses to the attention of the authors. |
|
Species Citation |
|
|
Author |
Bray, D.J. 2018 |
|
Resources |
Pontoh`s Pygmy Seahorse, Hippocampus pontohi Lourie & Kuiter 2008
References
Allen, G.R. & Erdmann, M.V. 2012. Reef fishes of the East Indies. Perth : Tropical Reef Research 3 vols, 1260 pp.
Gomon, M.F. & R.H. Kuiter 2009. Two new pygmy seahorses (Teleostei: Syngnathidae: Hippocampus) from the Indo-West Pacific. aqua, International Journal of Ichthyology 15(1): 37-44.
Hamilton, H., Saarman, N., Short, G., Sellas, A.B., Moore, B., T. Hoang, T., Grace, C.L., Gomon, M., Crow, K. & Simison, W.B. 2016. Molecular phylogeny and patterns of diversification in syngnathid fishes. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 107: 388-403 + supplement 1-4 + 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2016.10.003 Abstract
Kuiter, R.H. 2009. Seahorses and their relatives. Seaford, Australia : Aquatic Photographics pp. 331. (as Hippocampus pontohi & H. severnsi)
Lourie, S. 2016. Seahorses. A life-size guide to every species. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp. 1-160.
Lourie, S.A. & Kuiter, R.H. 2008. Three new pygmy seahorse species from Indonesia (Teleostei: Syngnathidae: Hippocampus). Zootaxa 1963: 54-68. (as Hippocampus pontohi & H. severnsi).
Lourie, S.A., Pollom, R.A. & Foster, S.J. 2016. A global revision of the seahorses Hippocampus Rafinesque 1810 (Actinopterygii: Syngnathiformes): taxonomy and biogeography with recommendations for further research. Zootaxa 4146(1): 1-66. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4146.1.1Abstract
Pollom, R. 2017. Hippocampus pontohi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T107261198A54909454. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T107261198A54909454.en. Downloaded on 03 August 2018.
Reijnen, B.T., S.E.T. van der Meij & L.P. van Ofwegen. 2011. Fish, fans and hydroids: host species of pygmy seahorses. ZooKeys 103: 1-26. PDF Open access
Short, G., Smith, R., Motomura, H., Harasti, D. & Hamilton, H. 2018. Hippocampus japapigu, a new species of pygmy seahorse from Japan, with a redescription of H. pontohi (Teleostei, Syngnathidae). ZooKeys 779: 27-49. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.779.24799 Open access