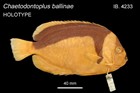
Ballina Angelfish, Chaetodontoplus ballinae Whitley 1959

A Ballina Angelfish, Chaetodontoplus ballinae, at Balls Pyramid, near Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea. Source: Peter Parker. License: All rights reserved
A striking angelfish with a black and white body, yellow pectoral and caudal fins, and yellow eyes. The species inhabits deeper reefs in eastern Australia and on the Lord Howe Rise in the Tasman Sea.
Video of a Ballina Angelfish at Balls Pyramid near Lord Howe Island.
Video of a Ballina Angelfish and Halfbanded Angelfish, Genicanthus semicinctus, at South East Rock, Balls Pyramid near Lord Howe Island (40 sec into video).
Ballina Angelfish, Chaetodontoplus ballinae Whitley 1959
More Info
|
Distribution |
Endemic to eastern Australia, and known from scattered localities including off Stradbroke Island, southern Queensland, northern New South Wales off Coffs Harbour, Ballina, Evans Head, North Solitary Island, Seal Rocks, and the Lord Howe Province in the Tasman Sea. Usually inhabits deeper coastal and offshore reefs, pinnacles and seamounts, at depths to 200 m. Ballina Angelfish are relatively common around Balls Pyramid near Lord Howe Island, where they can be seen in deeper areas with large boulders, rock stacks, pinnacles, caves and crevices. |
|
Size |
To 20 cm |
|
Colour |
Pearly white with a well-defined black band over the back and lower half of the dorsal fin, with the anterior end extending down as a bar over the pectoral-fin base; lips black, a dark bar through eye; anal fin, outer half of dorsal fin and pelvic fins white; eye, anterior dorsal-fin spines, caudal and pectoral fins yellow. |
|
Feeding |
Presumably an omnivore. Other species in the genus Chaetodontoplus feed on benthic invertebrates such as sponges, tunicates and algae. Some species also consume jellyfishes. |
|
Biology |
Almost nothing is known of the biology of this species. Individuals are often seen in pairs, and appear to occupy a home range. |
|
Fisheries |
Occasionally taken as bycatch in fishing operations. |
|
Conservation |
IUCN Red List: Least Concern NSW Fisheries Management Act 1994: Protected |
|
Similar Species |
With its black, white and yellow colour-pattern Ballina angelfish are unique in the genus Chaetodontoplus. |
|
Etymology |
The species is named for the type locality, Ballina, a coastal town in northern New South Wales. |
|
Species Citation |
Chaetodontoplus ballinae Whitley 1959, Proc. Roy. Soc. N. S. W. 1957–58: 21. Type locality: off Ballina Bar, New South Wales (caught in a trap). |
|
Author |
Bray, R.D. & Bray, D.J. 2020 |
|
Resources |
Ballina Angelfish, Chaetodontoplus ballinae Whitley 1959
References
Allen, G.R. 1980. Butterfly and angelfishes of the world. Volume II : 149-352.
Allen, G.R., Steene, R. & Allen, M. 1998. A guide to angelfishes and butterflyfishes. Odyssey Publishing / Tropical Reef Research, Perth, 250 pp
Coleman, N. 2002. Lord Howe Island Marine Park: sea shore to sea floor. World Heritage Wildlife Guide. Neville Coleman’s Underwater Geographic Pty Ltd.
Kuiter, R.H. 1993. Coastal Fishes of South-eastern Australia. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 437 pp.
Kuiter, R.H., Debelius, H. & Tanaka, H. 2003. Pomacanthidae, a Comprehensive Guide to Angelfishes. Melbourne : Zoonetics 206 pp.
Kuiter, R. & Kuiter, S. 2018. Coastal sea-fishes of south-eastern Australia. Seaford, Victoria : Aquatic Photographics, 371 pp.
Parker, P.G. 1994. Re-discovering the Ballina angelfish Chaetodontoplus ballinae (Pomacanthidae) Whitley, 1959: two new fish records for Lord Howe Island, Australia. Freshwater and Marine Aquarium (US): 112–115.
Pyle, R., Myers, R., Rocha, L.A. & Craig, M.T. 2010. Chaetodontoplus ballinae. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T165847A6147547. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T165847A6147547.en. Downloaded on 01 October 2020.
Randall, J.E., Allen, G.R. & Steene, R. 1990. Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 507 pp. figs.
Speare, P., Cappo, M., Rees, M., Brownlie, J. & Oxley, W. 2004. Deep water fish and benthic surveys in the Lord Howe Island Marine Park (Commonwealth Waters): February 2004. Townsville : Australian Institute of Marine Sciences 30 pp.
Steene, R.C. 1978. Butterfly and Angelfishes of the World. Australia. Sydney : A.H. & A.W. Reed Vol. 1 144 pp. 216 figs
Whitley, G.P. 1959. Ichthyological snippets. The Australian Zoologist 12(4): 310-323 figs 1-3
Whitley, G.P. 1959. More ichthyological snippets. Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales 1957–58: 11-26 figs 1-9. See ref at BHL