- Classification
- ACTINOPTERYGII
- PERCIFORMES
- CLINIDAE
- Heteroclinus
- macrophthalmus
Large-eye Weedfish, Heteroclinus macrophthalmus Hoese 1976
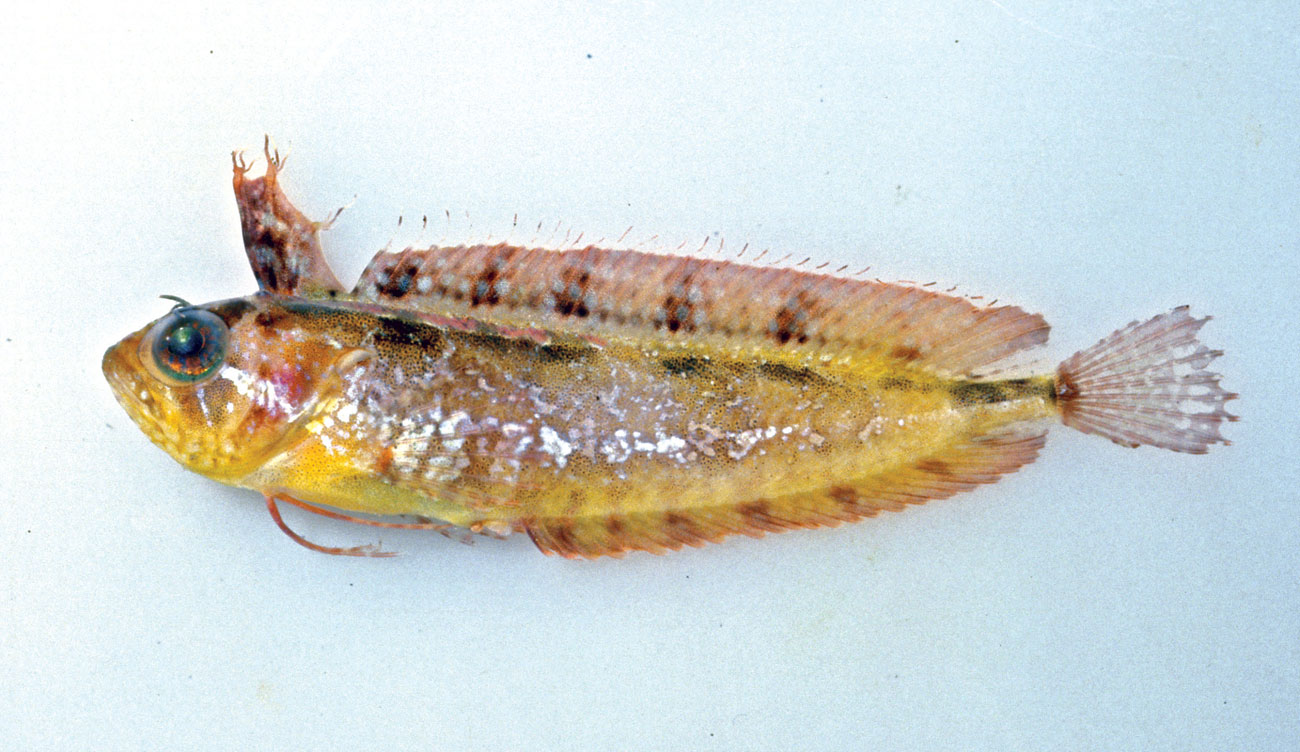

A Large-eye Weedfish, Heteroclinus macrophthalmus. Source: Rudie Kuiter / Aquatic Photographics. License: All rights reserved
The Large-eye Weedfish has broad, flattened orbital tentacles with 5-10 slender lobes at the tip, and short nasal tentacles with 3-6 elongate lobes.
Large-eye Weedfish, Heteroclinus macrophthalmus Hoese 1976
More Info
|
Distribution |
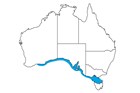
Endemic to southern Australia, from about Wilsons Promontory, Victoria, to the Recherche Archipelago, Western Australia, and northern Tasmania. Usually inhabits relatively deep seagrass beds and dense macroalgal beds at depths to 20 m. |
|
Features |
Dorsal fin III, XXIX-XXXI,4-5; Anal fin II,25-27; Caudal fin (segmented rays) 11; Pectoral fin 12-13; Pelvic fin I,2; Lateral line (arched portion) 23-28 + (straight portion) 13-24; Gill rakers 2-3 + 6-8 = 8-10. Body of moderate size (depth at anal fin origin 19-22% SL), strongly compressed; caudal peduncle very slender. Head of moderate to large size (28-30% SL); eyes large (10-11% SL); mouth large (upper jaw length 11-13% SL); 13 circumorbital pores arranged uniserially; each orbital tentacle broad, flattened with five to ten slender lobes at tip; nasal tentacles short with three to six elongate lobes; gill rakers simple. Scales cycloid on body; lateral line scales reaching well beyond pectoral fins but not reaching to caudal fin; anterior lateral line scales overlapping, each with single median posterior pore, posterior scales not overlapping, each with median pore at either end. Two dorsal fins, first dorsal slightly elevated (height 9-15% SL), originating over posterior end of preopercles, last spine connected to base of second dorsal fin; first three to four dorsal spines with two to six small, elongate, free flaps, rest of spines with single, elongate, free flap; last anal fin ray broadly connected to caudal peduncle; candal fin rounded (17-20% SL). Pectoral fins large, rounded. Pelvic fins jugular, thin, with two elongate soft rays (third ray rudimentary, visible only on dissection) reaching to about anal fin origin. |
|
Size |
Body of moderate size (depth at anal fin origin 19 22% SL), strongly compressed; caudal peduncle very slender. Head of moderate to large size (28 30% SL); eyes large (10 11% SL); mouth large (upper jaw length 11 13% SL); 13 circumorbital pores arranged uniserially; each orbital tentacle broad, flattened with five to ten slender lobes at tip; nasal tentacles short with three to six elongate lobes; gill rakers simple. Scales cycloid on body; lateral line scales reaching well beyond pectoral fins but not reaching to caudal fin; anterior lateral line scales overlapping, each with single median posterior pore, posterior scales not overlapping, each with median pore at either end. Two dorsal fins, first dorsal slightly elevated (height 9 15% SL), originating over posterior end of preopercles, last spine connected to base of second dorsal fin; first three to four dorsal spines with two to six small, elongate, free flaps, rest of spines with single, elongate, free flap; last anal fin ray broadly connected to caudal peduncle; candal fin rounded (17--20% SL). Pectoral fins large, rounded. Ventral fins jugular, thin, with two elongate soft rays (third ray rudimentary, visible only on dissection) reaching to about anal fin origin. |
|
Colour |
Head and body tan, with a dark brown stripe along back; stripe sometimes broken with 4-6 brown bars extending below; anterior lateral line scales often black. |
|
Conservation |
|
|
Similar Species |
Differs from the Adelaide Weedfish, Heteroclinus adelaidae, in having a larger eye, dorsal-fin spines with free lobes, branched nasal and orbital tentacles with numerous elongate lobes, more dorsal-, anal- and pectoral-fin rays, and more lateral line scales. |
|
Etymology |
The specific name macrophthalmus is from the Latin macro (= large) and ophthalmus (= eye), in reference to the larger eye of this species compared with that of Heteroclinus adelaidae. |
|
Species Citation |
Heteroclinus macrophthalmus Hoese, 1976, Aust. Zool. 19(1): 63, figs 3b, 5-7. Type locality: Port Lincoln, South Australia, depth 10-18 m. |
|
Author |
Bray, D.J. 2021 |
|
Resources |
Large-eye Weedfish, Heteroclinus macrophthalmus Hoese 1976
References
Hoese, D.F. 1976. A redescription of Heteroclinus adelaidae Castelnau (Pisces : Clinidae), with description of a related species. Australian Zoologist 19(1): 51-67 figs 1-7 See ref at BHL
Hoese, D.F., Gomon, M.F. & Rennis, D.S. 2008. Family Clinidae. pp. 696-722 in Gomon. M.F., Bray, D.J. & Kuiter, R.H (eds). Fishes of Australia's Southern Coast. Sydney : Reed New Holland 928 pp.
Kuiter, R.H. 1993. Coastal Fishes of South-eastern Australia. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 437 pp.
Kuiter, R.H. & Kuiter, S.L. 2018. Fish watchers guide to coastal sea-fishes of south-eastern Australia. Seaford, Victoria : Aquatic Photographics, 371 pp.
Last, P.R., Scott, E.O.G. & Talbot, F.H. 1983. Fishes of Tasmania. Hobart : Tasmanian Fisheries Development Authority 563 pp. figs.
Rennis, D., Hoese, D.F. & Gomon, M.F. 1994. Family Clinidae. pp. 741-775, figs 650-684B in Gomon, M.F., Glover, C.J.M. & Kuiter, R.H. (eds). The Fishes of Australia's South Coast. Adelaide : State Printer 992 pp. 810 figs.
Williams, J.T., Holleman, W. & Clements, K.D. 2014. Heteroclinus macrophthalmus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014: e.T178930A1549151. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T178930A1549151.en. Downloaded on 17 August 2016.