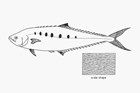
Needleskin Queenfish, Scomberoides tol (Cuvier 1832)
Other Names: Needlescaled Queenfish, Needle-scaled Queenfish, Slender Leatherskin
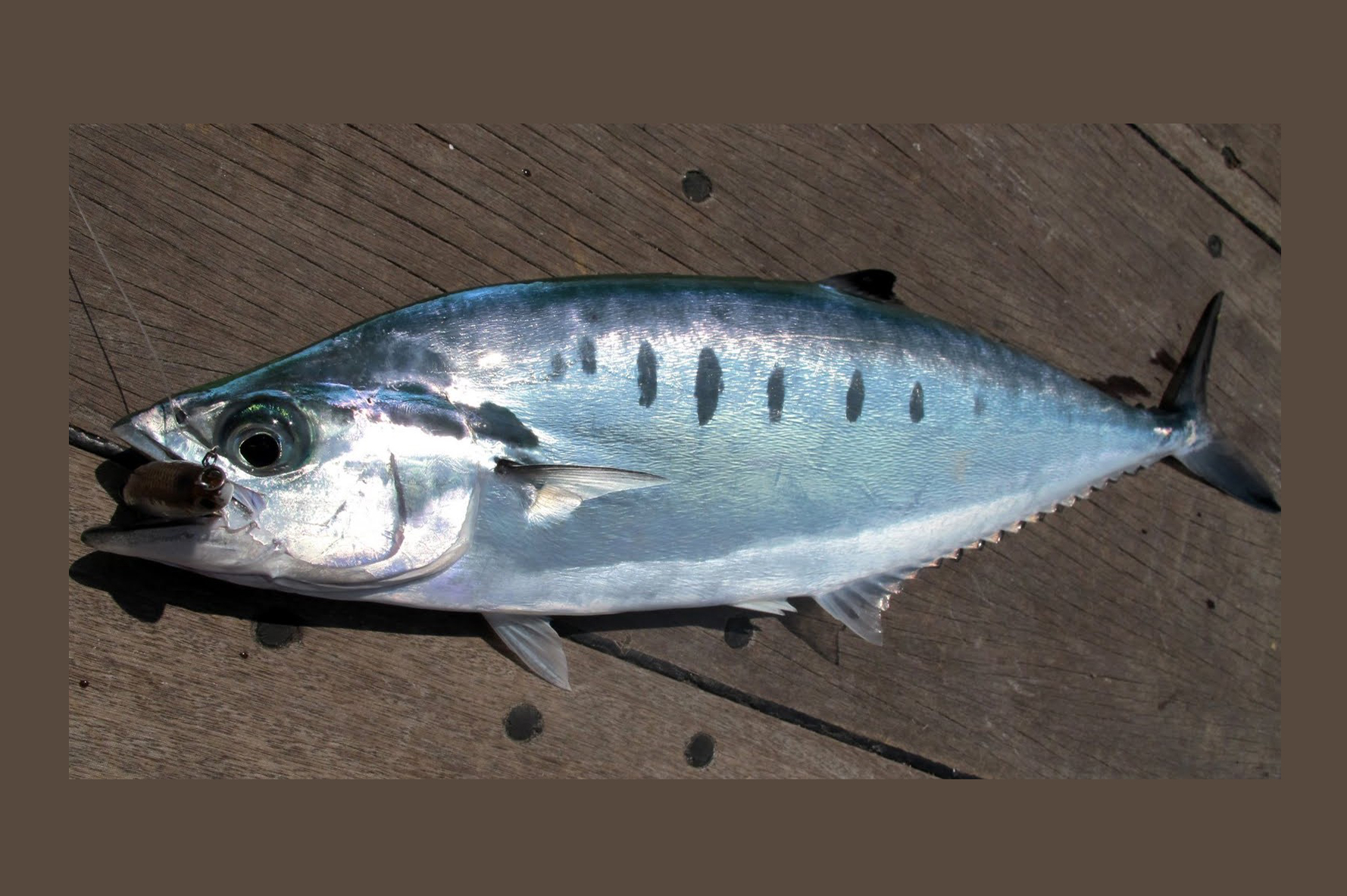

A Needleskin Queenfish, Scomberoides tol, from Port Douglas, Queensland, December 2011. Source: Kare Kare / Wikimedia Commons. License: CC by Attribution-ShareAlike
Summary:
A bluish-green to bluish-grey queenfish becoming silvery white below, with 5-8 vertically elongate or dark oval spots along the side, the first 4-5 intersecting the lateral line, a black outer half on the dorsal fin lobe, and a white anterior lobe on the anal fin. The upper jaw extends to the rear edge of the pupil in adults.
The spots along the side are faint or absent in juveniles.
The spots along the side are faint or absent in juveniles.
Cite this page as:
Bray, D.J. 2020, Scomberoides tol in Fishes of Australia, accessed 02 Jul 2025, https://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/4284
Needleskin Queenfish, Scomberoides tol (Cuvier 1832)
More Info
|
Distribution |
Northern Australia, from Cape Cuvier, Western Australia, north to Ashmore Reef and Cartier Island in the Timor Sea, and around the tropical north to the Gold Coast, Queensland, and possibly reefs in the Coral Sea. Elsewhere the species occurs in the tropical, Indo-west Pacific - from eastern Africa and the Persian Gulf, to Tonga, north to southern Japan, south to northern Australia and New Caledonia. Inhabits estuaries and coastal waters, often forming small schools. |
|
Features |
Dorsal fin VI-VII + I, 19-21; Anal fin A II + I, 18-22; Gill rakers 4-7 + 17-20 = 21-26; V 10+16. Body strongly compressed, oblong and elliptical, dorsal and ventral profiles equally convex; upper jaw extending to posterior edge of pupil in adults; dentary with 2 teeth rows separated by a shallow groove in adults, teeth in both rows almost same size. Body covered with slender, needle-like scales; no scutes along lateral line. Soft rays of posterior dorsal and anal fins consist of semi-detached finlets. |
|
Colour |
Bluish above, silver or white ventrally, with 5-8 vertically oblong or oval black spots, the first 4-5 intersect the lateral line, dorsal fin lobe black outer half. |
|
Feeding |
Adults mainly consume fishes, while juveniles use specialised rasping teeth to feed on the scales and epidermal tissues of other fishes. |
|
Fisheries |
Targeted by commercial and recreational fishers. Throughout its range, this species is taken using drift set nets, gill nets, seines and hook and line, and is mainly marketed fresh; also used as baitfish in some areas. |
|
Species Citation |
Chorinemus tol Cuvier, in Cuvier & Valenciennes 1832, Histoire Naturelle des Poissons Vol. 8: 385. Type locality: Malabar Coast, India. |
|
Author |
Bray, D.J. 2020 |
|
Resources |
Needleskin Queenfish, Scomberoides tol (Cuvier 1832)
References
Allen, G.R. 1997. Marine Fishes of Tropical Australia and South-east Asia. Perth : Western Australian Museum 292 pp. 106 pls.
Allen, G.R. & Erdmann, M.V. 2012. Reef fishes of the East Indies. Perth : Tropical Reef Research 3 vols, 1260 pp.
Allen, G.R. & Swainston, R. 1988. The Marine Fishes of North-Western Australia. A field guide for anglers and divers. Perth, WA : Western Australian Museum vi 201 pp., 70 pls.
Blaber, S.J.M. 1980. Fish of the Trinity Inlet System of North Queensland with notes on the ecology of fish faunas of tropical Indo-Pacific estuaries. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 31: 137-146.
Blaber, S.J.M., Brewer, D.T. & Salini, J.P. 1995. Fish Communities and the Nursery Role of the Shallow Inshore Waters of a Tropical Bay in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 40: 177-193.
Blaber, S.J.M., Young, J.W. & Dunning, M.C. 1985. Community structure and zoogeographic affinities of the coastal fishes of the Dampier region of north-western Australia. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 36: 247-266.
Cuvier, G.L. in Cuvier, G.L. & Valenciennes, A. 1832. Histoire Naturelle des Poissons. Paris : Levrault Vol. 8 509 pp. pls 209-245. See ref at BHL
Gloerfelt-Tarp, T. & Kailola, P.J. 1984. Trawled Fishes of Southern Indonesia and Northwest Australia. Jakarta : Dir. Gen. Fish. (Indonesia), German Tech. Coop., Aust. Dev. Ass. Bur. 406 pp.
Grant, E.M. 1975. Guide to Fishes. Brisbane : Queensland Government, Co-ordinator General’s Department 640 pp.
Johnson, J.W. 1999. Annotated checklist of the fishes of Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 43(2):709-762.
Johnson, J.W. 2010. Fishes of the Moreton Bay Marine Park and adjacent continental shelf waters, Queensland, Australia. pp. 299-353 in Davie, P.J.F. & Phillips, J.A. Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Marine Biological Workshop, The Marine Fauna and Flora of Moreton Bay. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 54(3)
Kimura, S., Iwatsuki, Y. & Kojima, J.-I.. 1998. Descriptive morphology of the juvenile stages of two Indo-Pacific carangids, Scomberoides lysan and Scomberoides tol (Pisces: Perciformes) Copeia 1998(2): 510-515 https://www.jstor.org/stable/1447453
Larson, H.K., Williams, R.S. & Hammer, M.P. 2013. An annotated checklist of the fishes of the Northern Territory, Australia. Zootaxa 3696(1): 1-293
Pepperell, J. 2010. Fishes of the Open Ocean a Natural History & Illustrated Guide. Sydney : University of New South Wales Press Ltd 266 pp.
Ramm, D.C., Pender, P.J., Willing, R.S. & Buckworth, R.C. 1990. Large-scale spatial patterns of abundance within the assemblage of fish caught by prawn trawlers in Northern Australian waters. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 41(1): 79-95.
Randall, J.E. 2005. Reef and shore fishes of the South Pacific. New Caledonia to Tahiti and the Pitcairn Islands. Honolulu : University of Hawaii Press 707 pp.
Randall, J.E., Allen, G.R. & Steene, R. 1990. Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 507 pp. figs.
Randall, J.E., Allen, G.R. & Steene, R. 1997. Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Bathurst : Crawford House Press 557 pp. figs.
Russell, B.C. & Houston, W. 1989. Offshore fishes of the Arafura Sea. The Beagle, Records of the Museums and Art Galleries of the Northern Territory 6(1): 69-84
Russell, B.C., Larson, H.K., Hutchins, J.B. & Allen, G.R. 2005. Reef fishes of the Sahul Shelf. The Beagle, Records of the Museums and Art Galleries of the Northern Territory Supplement 1 2005: 83-105
Sainsbury, K.J., Kailola, P.J. & Leyland, G.G. 1984. Continental Shelf Fishes of Northern and North-Western Australia. Canberra : Fisheries Information Service 375 pp. figs & pls.
Smith-Vaniz, W.F. 1999. Family Carangidae. pp. 2659-2756 in Carpenter, K.E. & Niem, T.H. (eds). The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific. FAO Species Identification Guide for Fisheries Purposes. Rome : FAO Vol. 4 pp. 2069-2790.
Smith-Vaniz, W.F. & Staiger, J.C. 1973. Comparative revision of Scomberoides, Oligoplites, Parona, and Hypacanthus with comments on the phylogenetic position of Campogramma (Pisces : Carangidae). Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences 39(13): 185-256 figs 1-26 See ref at BHL
Smith-Vaniz, W.F. & Williams, I. 2016. Scomberoides tol (errata version published in 2017). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T20435185A115382256. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T20435185A46664124.en. Downloaded on 5 December 2018.