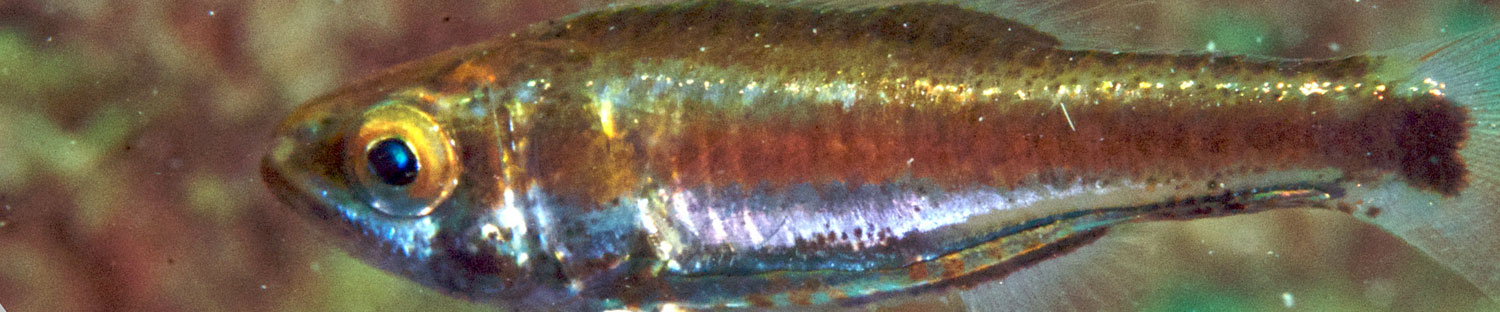
Genus Siphamia
A small Indo-Pacific genus with 23 species. Siphamia is unique among apogonids in having a bacterial bioluminescent system and spinoid scales (except for the Australian endemics S. cephalotes and S. cuneiceps which differ from all other Siphamia in having ctenoid scales and a distinctly elongate body) (Gon & Allen 2012).
Body short, compressed to relatively slender, depth 2.2–4.8 in SL, width 1.6–2.8 in depth; eye large to moderate, snout moderate to short; pectoral and pelvic fins moderately long; caudal peduncle stout to somewhat slender.
Preopercular edge smooth to fully serrate (up to 38 serrations); preopercular ridge smooth. Scales usually spinoid, sometimes cycloid or ctenoid. Lateral-line scales usually with a vertical row of free neuromasts.
Gon & Allen (2012) recently revised the genus, describing nine new species.
References
Allen, G.R. & Gomon, M.F. 2008. Family Apogonidae. pp. 557-561 in Gomon. M.F., Bray, D.J. & Kuiter, R.H (eds). Fishes of Australia's Southern Coast. Sydney : Reed New Holland 928 pp.
Gon, O. & G.R. Allen. 2012. Revision of the Indo-Pacific cardinalfish genus Siphamia (Perciformes: Apogonidae). Zootaxa 3294: 1–84. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3294.1.1
Kuiter, R.H. & Kozawa, T. 2019. Cardinalfishes of the world. New Edition. Seaford, Victoria: Aquatic Photographics, and Okazaki, Aichi: Anthias (Nexus), 198 pp.
Leis, J.M. & Bullock, S. 1986. The luminous cardinalfish Siphamia (Pisces, Apogonidae): development of larvae and the luminous organ, pp. 703–714 in Uyeno, T., Arai, R., Taniuchi, T., & Matsuura, K. (Eds.), Indo Pacific Fish Biology: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Indo-Pacific Fishes. Ichthyological Society of Japan.